
Overview of Japanese taxation for individuals
Individual income tax in Japan consists of national income tax and local inhabitant tax. The taxable year of individual income tax is the calendar year, while local inhabitant tax is assessed on individuals who live in Japan as of 1 January. Inhabitant tax is calculated based on income for the preceding year.
Individuals who sell and acquire goods and services in Japan will suffer consumption tax on those transactions. In principle, consumption taxpayer status is determined depending on the amount of domestic taxable sales in the past. Japanese consumption tax is sales based tax and is similar to VAT/GST.
Classification of individual taxpayers
There are two categories of individual taxpayers – Resident or non-resident. Below is the definition.
Resident:
Residents are divided to either permanent resident or non-permanent resident.
A non-permanent resident is an individual who doesn’t have Japanese nationality and has lived in Japan for 5 years or less in the last 10 years.
A permanent resident is an individual other than a non-permanent resident, i.e. an individual who has Japanese nationality, or has lived in Japan for more than 5 years in the last 10 years. Permanent resident is subject to Japanese income taxes on worldwide income.
Non-resident:
A non-resident is an individual other than a resident. Basically, an individual who does not have an address in Japan and has lived in Japan for less than 1 year.
Short term visitors
Generally, Japan’s double tax treaties are in line with OECD model treaty regarding the treatment of tax exempt foreign employees temporally working in Japan. Such employees are generally tax-exempt if they meet the following 3 criteria:
・They are present in Japan for less than 183 days in any 12 month period
・Their salary is paid by a non-resident employer
・There aren’t any salary paid by a permanent establishment (PE) in Japan
This criteria depends on each country’s tax treaty, so please refer to the double tax treaty of your country.
Tax rate
Japanese income tax use the progressive tax rate. The following rates are applied to the income (revenue-expenses) minus allowable tax deductions. (2015~)
National income tax rate
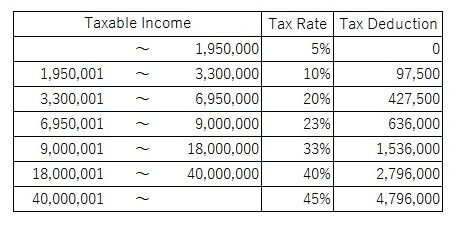
Example
If your taxable income is JPY7,000,000, income tax amount is following:
7,000,000×0.23-636,000=974,000
Local tax rate
Local tax consists of two categories – per capita levy and income-based levy. Per capita tax is around JPY5,000/year depending on each municipal government. Inhabitant tax rate is 10%, regardless of the amount of taxable income. A non-resident is generally not liable for inhabitant tax, however if a non-resident is registered in the municipal government and lives in Japan as of 1 January, the individual may be liable for inhabitant tax.
Generally, inhabitant tax returns are not required to be filed since the information necessary for assessment is submitted by your employer or by filing income tax returns.